In the fast-paced world of software development, the ability to deliver high-quality applications quickly and efficiently is paramount. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) are practices that have revolutionized the development process, enabling teams to build, test, and release software faster and with fewer errors. This blog will explore what CI/CD is, why it's important, and how you can implement it in your development workflow.
What is CI/CD?
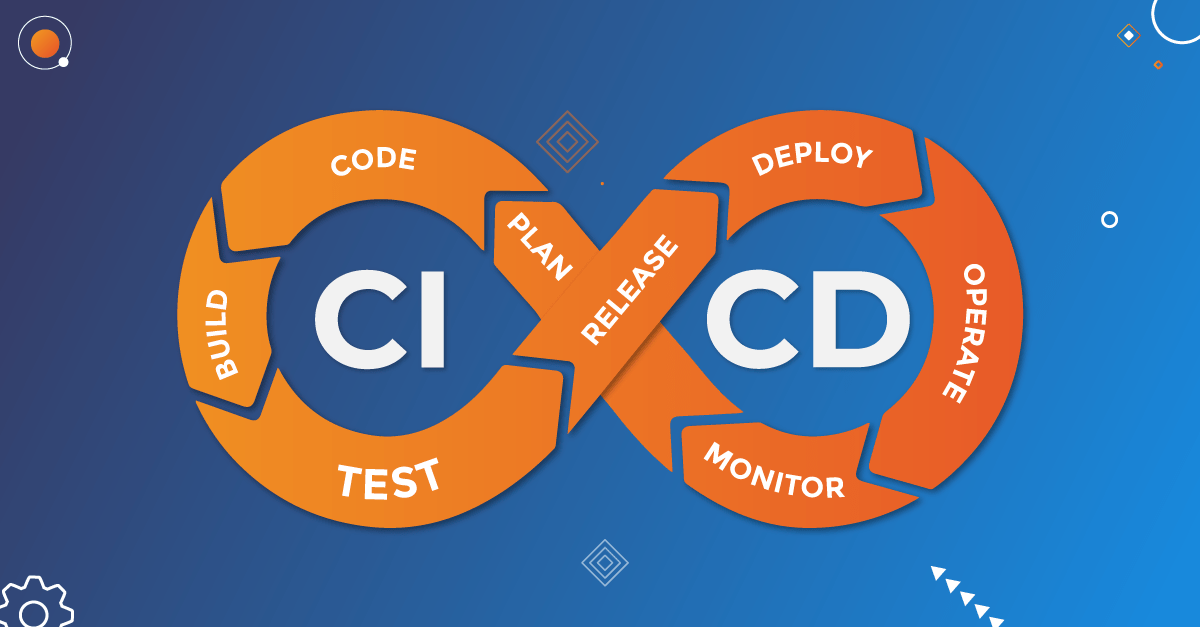
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (or Continuous Delivery). These are two fundamental DevOps practices that aim to improve the process of software development, integration, and delivery.
Continuous Integration (CI): CI is the practice of automatically integrating code changes from multiple contributors into a shared repository several times a day. Each integration is verified by an automated build and automated tests, allowing teams to detect and fix integration issues early.
Continuous Deployment (CD): CD takes CI a step further by automatically deploying every change that passes the automated tests to production. This ensures that the software is always in a deployable state, enabling frequent and reliable releases to end users.
Why is CI/CD Important?
Faster Time to Market: CI/CD automates many of the manual steps involved in the development process, significantly reducing the time it takes to release new features and updates.
Improved Code Quality: By integrating and testing code frequently, CI/CD helps identify and resolve bugs early, leading to higher-quality software.
Increased Collaboration: CI/CD encourages collaboration among team members by providing a consistent and automated process for integrating and deploying code changes.
Reduced Risk: Automated testing and deployment reduce the risk of human error and ensure that the software is always in a deployable state.
Scalability: CI/CD pipelines can scale to accommodate large teams and complex projects, ensuring that the development process remains efficient and manageable.
Implementing CI/CD in Your Workflow
Set Up a Version Control System: The foundation of CI/CD is a version control system (VCS) like Git. Ensure that your codebase is stored in a VCS and that all team members are using it consistently.
Choose a CI/CD Tool: There are many CI/CD tools available, such as Jenkins, CircleCI, Travis CI, GitLab CI/CD, and GitHub Actions. Select a tool that fits your team's needs and integrates well with your existing tools and workflows.
Define Your Pipeline: A CI/CD pipeline consists of a series of stages that code changes go through before being deployed to production. Common stages include:
- Build: Compile the code and create artifacts.
- Test: Run automated tests to verify the code.
- Deploy: Deploy the code to staging and production environments.
Automate Testing: Write automated tests for your code and integrate them into your CI/CD pipeline. Unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests are all important for ensuring code quality.
Monitor and Iterate: Continuously monitor your CI/CD pipeline for performance and reliability. Collect feedback from your team and make improvements as needed.
Best Practices for CI/CD
Commit Code Frequently: Encourage developers to commit code changes frequently to ensure that the codebase is always up-to-date and integration issues are caught early.
Keep Builds Fast: Optimize your build and test processes to keep the CI/CD pipeline fast and responsive. Consider parallelizing tasks and using caching where possible.
Fail Fast, Fix Fast: Set up your pipeline to fail early if any issues are detected. This allows developers to address problems quickly and prevents faulty code from reaching production.
Use Feature Flags: Feature flags allow you to deploy new features to production without immediately making them available to users. This can be useful for testing and gradual rollouts.
Conclusion
CI/CD is a game-changer for modern software development, enabling teams to deliver high-quality software faster and more reliably. By automating the integration, testing, and deployment processes, CI/CD reduces the risk of errors, improves collaboration, and accelerates time to market. Whether a small startup or a large enterprise, implementing CI/CD can help you stay competitive in today's rapidly evolving technology landscape.
Ready to unleash the power of CI/CD in your development workflow? Start by setting up a robust CI/CD pipeline and watch your development process become more efficient and agile.
Example 1: Setting Up a Basic CI/CD Pipeline with GitHub Actions
Let's say you have a simple web application written in Node.js. You want to set up a CI/CD pipeline using GitHub Actions to automate the process of building, testing, and deploying your application.
Create a GitHub Repository:
- Push your Node.js project to a new GitHub repository.
Set Up GitHub Actions:
- Create a new file in your repository at
.github/workflows/ci-cd.yml.
- Create a new file in your repository at
Define Your CI/CD Workflow:
In this example, the pipeline runs whenever you push code to the main branch. It performs the following steps:
- Check out the code from the repository.
- Sets up Node.js.
- Installs dependencies.
- Runs tests.
- Deploys the application to Heroku if the tests pass.
Example 2: Using CircleCI for a Python Application
Imagine you have a Python application and you want to set up a CI/CD pipeline using CircleCI.
Create a CircleCI Configuration File:
- Add a
.circleci/config.ymlfile to your repository.
- Add a
Define Your CircleCI Configuration:
This CircleCI configuration defines a workflow with two jobs:
- The
buildjob checks out the code, installs dependencies, and runs tests. - The
deployjob deploys the application to an AWS S3 bucket if the build and tests pass.
Comments
Post a Comment